3.2- Fault Detection and Rectification Decision-Making
In the previous tests, we verified NCE-FabricInsight’s ability to define intent-based monitoring tasks and track the health status of services and traffic paths. In this test, we aim to evaluate its capability to detect network issues, suggest appropriate solutions, and, where applicable, resolve them automatically.
To achieve this, we introduced multiple issues into the network and monitored the response of NCE-FabricInsight.
Packetloss
In this scenario, we installed an impairment device between BorderLeaf1 and Spine1, using a 10G link due to the impairment device's interface limitation. The original 100G link was temporarily replaced to enable this test scenario. The telemetry data was collected using In-situ Flow Information Telemetry (IFIT). It is important to note that IFIT collects data only for L3 interfaces, so telemetry for Leaf-Spine traffic was not included in this test.
The impairment was configured as unidirectional packet loss at 10% for all traffic streams on the link. NCE-FabricInsight reported a packet loss rate of 7%, which is reasonably close given the passive nature of telemetry collection.
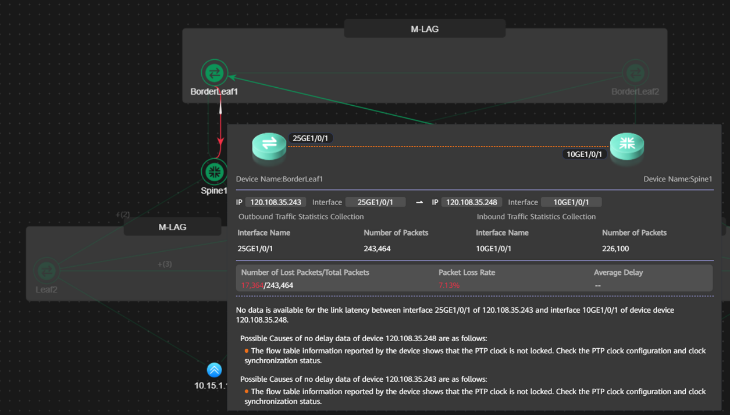
Figure 30: Link Operational Metrics - Packet Loss Rate
Latency data was not available, as Precision Time Protocol (PTP) was not enabled on the network devices. The system also did not provide a specific root cause for the packet loss, as link-based impairments are not directly linked to application flows. For comparison, a hardware issue such as an SFP with low optical power would have been reported under the system’s issue detection logic.
Link Flapping
We introduced link flapping to the network by repeatedly shutting down and re-enabling interface 1/0/1 on Leaf2, which connects to Spine1. The simulation consisted of ten shutdown and undo shutdown cycles, each spaced 10 seconds apart.
NCE-FabricInsight is configured to detect flapping if ten such events occur within a three-minute window. This threshold is adjustable. During the initial run, the device timestamps were inconsistent due to incorrect time zone settings and missing NTP synchronization, which affected detection accuracy. The test was repeated after Huawei configured NTP on the devices, using NCE-FabricInsight as the time source.
The system correctly identified the issue this time, reporting two issues, one related to the leaf switch and one related to the spine, as shown in Figure 31.
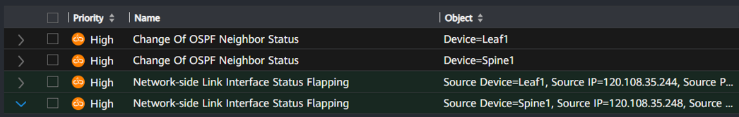
Figure 31: Link Flapping Issue
Expanding the issue shown in the previous figure provided additional details, including a repair recommendation, as illustrated in Figure 32.
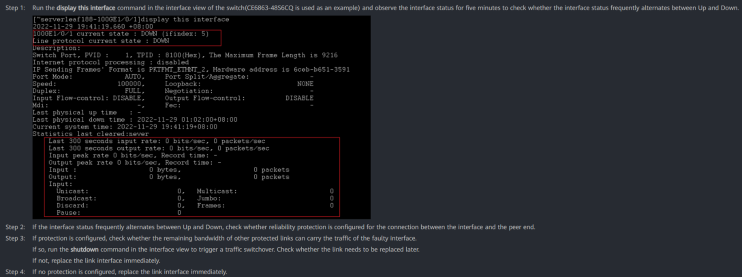
Figure 32: Link Flapping Repair Advice
The provided repair advice focused on manual steps to resolve the issue, which is helpful in environments where only NCE-FabricInsight is deployed.
NCE-FabricInsight redirected us to NCE-Fabric to automatically resolve the issue. Two options were shown: shutting down the interface on either the leaf or the spine, as shown in Figure 33.
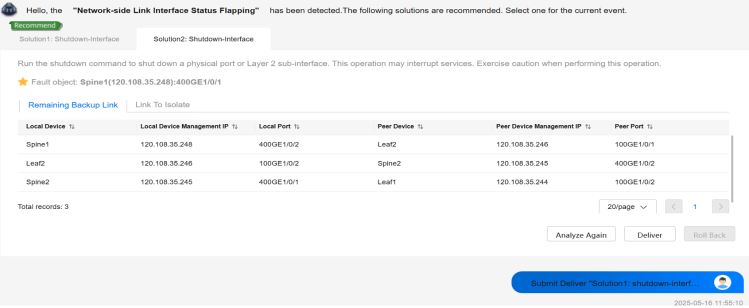
Figure 33: Link Flapping Automatic Repair
We proceeded with one of the options. The selected configuration was successfully delivered, and the system also analyzed the remaining backup paths.
After the solution was delivered, a rollback option was available in case the implemented action did not resolve the issue. In our case, we rolled back the solution configuration because the issue was artificially introduced. The rollback went without any problems.
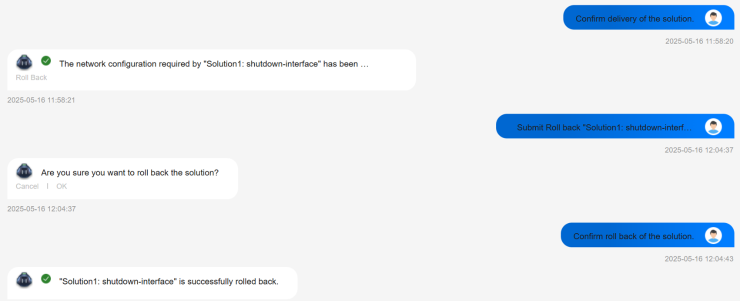
Figure 34: Rollback the Automatic Repair Change
The conversation between the user and the NCE-Fabric shown in Figure 34 is not text-based; the user does not type the messages highlighted in blue. Instead, these messages appear automatically after selecting one of the predefined options displayed beneath the white-highlighted messages.
IP Conflict
We created another issue by assigning the same IP address to two virtual machines—one on Leaf3 and one on Leaf4—both part of a Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation (MLAG) configuration. NCE-FabricInsight detected the duplicate IP issue as shown in Figure 35
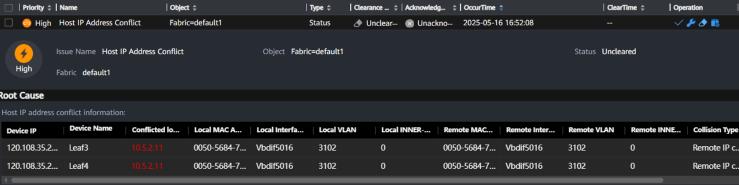
Figure 35: Duplicated IP Address Issue
The system also suggested recommended actions to resolve the issue, including multiple steps and specific CLI commands as shown in Figure 36. However, in this case, automatic delivery of the solution was not supported, likely due to the operational risks associated with modifying active MLAG configurations.
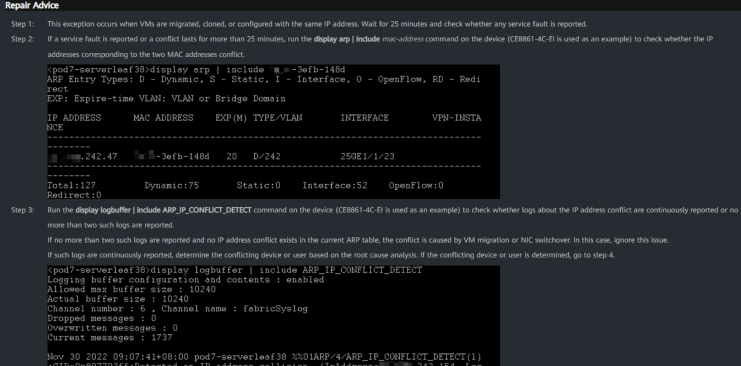
Figure 36: Duplicated IP Address Repair Advice
Routing Loop
To simulate a routing loop, we manually configured a static route on Spine2 that conflicted with an OSPF-learned route on the border leaf. This inconsistency created a routing loop in the network. NCE-FabricInsight successfully detected the loop and reported it. The diagnostic output included a basic recommendation to verify the static routing configuration. However, no automated solution delivery was available for this issue, and resolution required manual action.
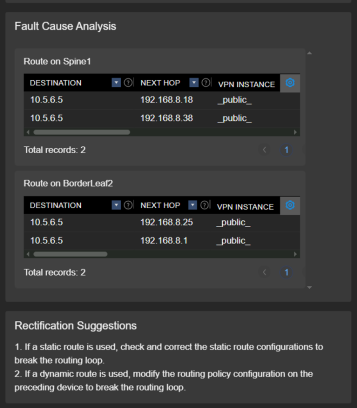
Figure 37: Routing Loop Analysis and Repair Suggestion
Security Policy Conflict
In this test, we configured a firewall rule to deny traffic to a specific address. NCE-FabricInsight detected the resulting connectivity issue and correctly flagged the traffic path as unreachable. The system identified the root cause as security policy-based filtering, as shown in the intercepted packets section. It provided detailed context, including source and destination IP addresses. The corresponding security rule “ENTAC” was highlighted in the configuration diff view, where the action was set to deny for the specified destination address.
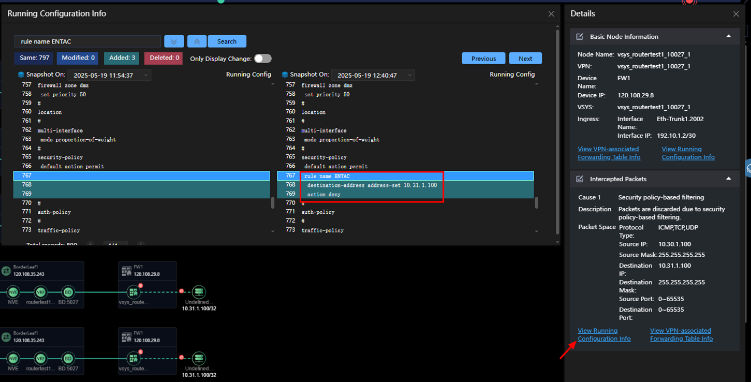
Figure 38: Security Policy Issue
Similar to the suggestion in the previous issue, NCE-FabricInsight provided repair guidance, instructing the user to check the security configurations by clicking View Running Configuration Info in the Details area to verify whether the device had rules blocking packets. While the resolution was not delivered automatically, the system offered clear and actionable guidance that helped identify the misconfigured policy.
Faulty Optical
To emulate a faulty optical module or fiber, we connected a traffic generator to a border leaf switch and configured the corresponding routing interface. The traffic generator was set to inject FEC (Forward Error Correction) errors into the transmitted frames, simulating the behavior of a degraded optical link. NCE-FabricInsight successfully detected the issue, identified the exact physical interface where the errors were observed, and provided repair suggestions, such as cleaning the optical module or replacing it if the problem persisted.
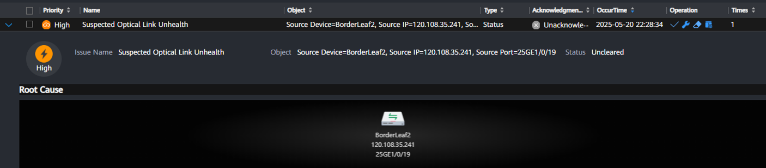
Figure 39: Faulty Optical Module Issue
NCE-FabricInsight successfully detected all the issues we introduced into the network and provided detailed diagnostic information, including rectification suggestions with CLI commands and step-by-step guidance. However, automatic implementation of these solutions was only supported in the case of link flapping. The platform required manual actions for other issues, such as IP conflicts and routing loops. Additionally, NCE-FabricInsight does not support simulating the proposed solutions before applying them, which limits its ability to meet the requirements for full automation.
Huawei stated that the NCE-Fabric, in collaboration with the NCE-FabricInsight, already supports a variety of issues for which an automatic repair can be generated, simulated, and implemented. The following table shows a full list of those issues and the rectification solution.
| Event Name | Rectification Plan |
|---|---|
| Intermittent Link Disconnection | Isolate the ports at both ends of the link. |
| Unidirectional Link Connectivity Fault on Network Side of a Switch | Isolate the port. |
| Switch Physical Port Suspended | Isolate the physical ports of the switch. |
| Suspected Optical Link Fault | Isolate the port. |
| Repeated Switch LPU Fault | Isolate LPUs. |
| Traffic Exception Caused by Switch Entry Inconsistency Between the Software Table and Hardware Table | Re-deliver specified entries in the software table to the hardware table. Restart the board. Restart the switch. |
| Traffic Exception Caused by Lost Switch Routing Hardware Tables | Re-deliver specified entries in the software table to the hardware table. Restart the board. Restart the switch. |
| Neighbor Relationship Flapping Due to an Incorrect Update Packet Received by Switch | Isolate the peer. |
| IP Address Conflict on Network Access Side | Display the conflict IP address or the port of the conflict IP address. Then isolate the specific IP address or port. |
| Suspicious Layer 2 Loop | Isolate the port. |
Server Access Fault | Restart the port. |
| Repeated Switch Restarts | Isolate the switch. |
| Two Master Switches in M-LAG | Isolate the switch. |
| The protocol status of the port is down | Isolate the port. |
| TCP SYN Flood Attack | Isolate the VM. Isolate the port. |
| ARP Attack | Isolate the VM. Isolate the port. |
| ND Attack | Isolate the VM. Isolate the port. |
| Flow Exception Caused by CE Switch Chip Soft Failure | Restart the switch. |
| OSPF Router ID Conflict | Configure a router ID for the device. |
| Designated Router IP Address Conflict | Reconfigure the IP address of the interface where a conflict occurs. |
| IP Address Conflict on Network Side | Shut down the port. |
| Invalid ARP Packet Received by Switch | Shut down the port and isolate the IP address. |
However, due to time constraints, those have not been tested in the scope of this evaluation.
Based on the observations in this test, NCE-FabricInsight fulfills Level 3 requirements for the capabilities of Fault Diagnosis, Solution Generation and Decision-Making, and Solution Implementation as defined in the ETSI GR ENI 049 specification.
| < Previous | Next > |
